Understanding Stem Cell Research
What's a stem cell?
The foundational building blocks of living organisms,
stem cells
Cells that have the ability to differentiate into multiple types of cells and make an unlimited number of copies of themselves.
stem cells
Cells that have the ability to differentiate into multiple types of cells and make an unlimited number of copies of themselves. are defined by two characteristics:
- They can make copies of themselves, or self-renew
- They can differentiate, or develop into more specialized cells
In humans, there are different types of stem cells that originate from different parts of the body and emerge during different times in our lives. These include embryonic stem cells Pluripotent stem cells that give rise to every cell type in the adult body. They are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. embryonic stem cells Pluripotent stem cells that give rise to every cell type in the adult body. They are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst., which only exist during the earliest stages of development, and tissue-specific stem cells Mature stem cells that are found in many adult organs and tissues (such as the brain and muscles). Unlike pluripotent stem cells, they can only produce the cell types found in the organ or tissue they inhabit. They're responsible for replacing cells that have been lost due to natural wear and tear, injury and illness throughout life; however, their ability to do so decreases with age. tissue-specific stem cells Mature stem cells that are found in many adult organs and tissues (such as the brain and muscles). Unlike pluripotent stem cells, they can only produce the cell types found in the organ or tissue they inhabit. They're responsible for replacing cells that have been lost due to natural wear and tear, injury and illness throughout life; however, their ability to do so decreases with age., which arise during fetal development and persist throughout life.
"Stem cells are the foundation of organisms, the stalk from which everything buds and branches.”
Alexander Capron
Bioethicist, World Health Organization
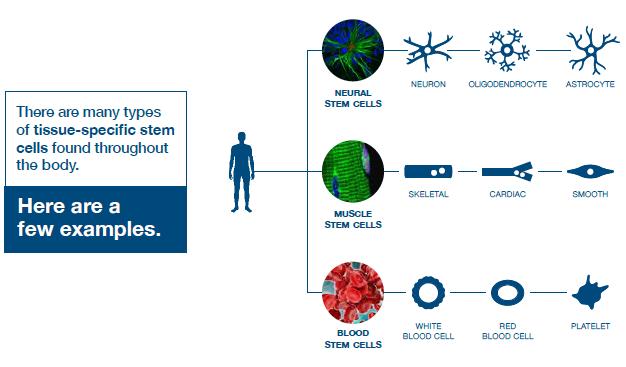
What are the different types of stem cells?
Tissue-Specific Stem Cells
Tissue-specific stem cells, sometimes referred to as adult or somatic stem cells, contribute to the body’s ability to create new cells that can restore damaged organs and tissues. They also replace cells that are lost in normal day-to-day living.
Scientists now know that small populations of tissue-specific stem cells reside in many organs and tissues, including the brain, skeletal muscle, skin, heart, intestines and liver. While tissue-specific stem cells can help the body repair by producing all the cell types within their designated tissues, their ability to regenerate is limited and decreases over time.
Blood stem cells A type of tissue-specific stem cells found in the blood and bone marrow that can form various types of mature blood and immune cells. These cells play a crucial role in maintaining the body's blood supply and immune system by continuously producing new blood cells throughout a person's life. Blood stem cells A type of tissue-specific stem cells found in the blood and bone marrow that can form various types of mature blood and immune cells. These cells play a crucial role in maintaining the body's blood supply and immune system by continuously producing new blood cells throughout a person's life., also known as hematopoietic stem cells, are found in the bone marrow and generate the different kinds of blood cells needed over a person’s lifespan. This includes red blood cells, white blood cells — also known as immune cells — and platelets. Transplants of blood stem cells have been used to treat patients with blood and immune diseases such as leukemia and aplastic anemia for more than 50 years. Today, the sources of blood stem cells used for transplantation include bone marrow, umbilical cord blood and peripheral blood.
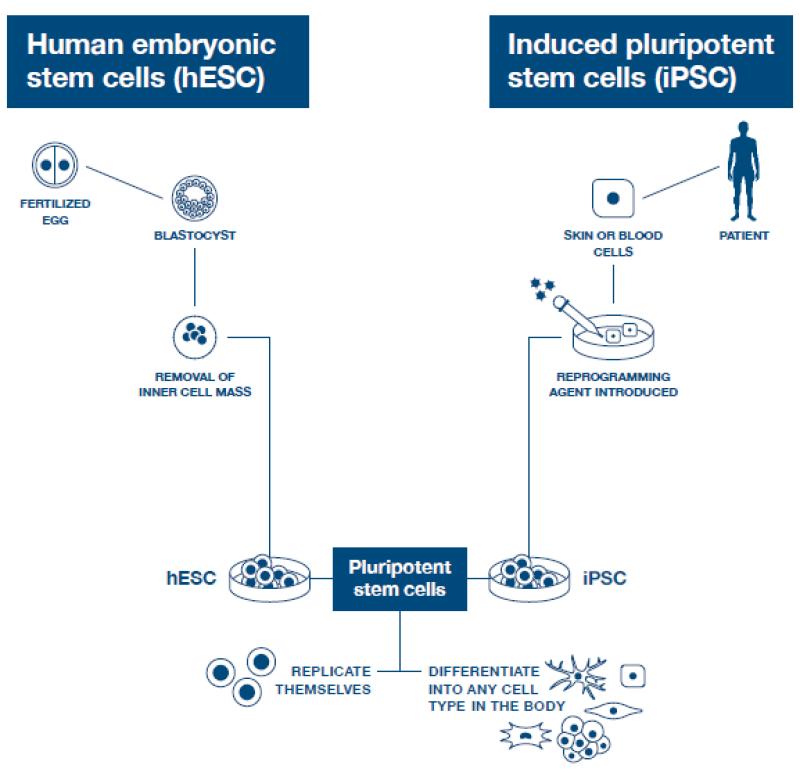
Human Embryonic Stem Cells
In 1998, scientists succeeded in isolating human embryonic stem cells, or hESCs, for the first time. Since then, the more versatile and flexible regenerative potential of hESCs has proved vital to scientific research, enabling scientists to learn about human developmental processes that would otherwise be inaccessible. Unlike tissue-specific stem cells, hESCs have two distinct capabilities: They can replicate indefinitely, and they’re pluripotent, meaning they can produce the more than 200 cell types found in the human body through a process called differentiation The process by which stem cells transform into specific, specialized cell types with distinct functions and features. differentiation The process by which stem cells transform into specific, specialized cell types with distinct functions and features..
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells iPS cells are cells taken from a patient that are reprogrammed so that they can undergo differentiation into any type of cell in the body. By maintaining the genetic code of the patient, iPS cells play a crucial role in disease modeling and regenerative medicine. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells iPS cells are cells taken from a patient that are reprogrammed so that they can undergo differentiation into any type of cell in the body. By maintaining the genetic code of the patient, iPS cells play a crucial role in disease modeling and regenerative medicine.
In 2006, a team in Japan showed it was possible to induce pluripotency in mature cells, creating what are known as induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPSCs. Shortly after, center members Drs. Kathrin Plath, William Lowry, Amander Clark and April Pyle were the first in California to report the successful generation of iPSCs.
iPSCs originate from cells — such as skin or blood — that are removed from a person and reprogrammed back to a pluripotent state. Like hESCs, these reprogrammed cells can replicate indefinitely as well as differentiate into any cell type in the human body. Since iPSCs are made from a patient’s own cells, therapies created from these cells could potentially be perfectly matched to the patient.
How are stem cells used in research?
Visit our Research Area pages to learn how our multidisciplinary teams of scientists, clinicians and engineers are conducting stem cell research that’s driving medical and scientific knowledge in new directions, fundamentally changing the understanding and treatment of disease.
Where do we get stem cells for research?
All of the human embryonic stem cells currently used in research come from cell lines that have been approved for research and registered with the National Institutes of Health. The original hESCs used to establish these lines come from embryos that are donated from consenting individuals or couples who have unused embryos after in vitro A process, procedure or study performed in a test tube or lab dish rather than in a living organism. in vitro A process, procedure or study performed in a test tube or lab dish rather than in a living organism. fertilization, or IVF, procedures. The embryonic stem cells are isolated from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst An embryo in its very early stage, usually 5 to 6 days old, that has not implanted or attached to a uterus. It is made up of a small group of inner cells, which will develop into the embryo, and an outer layer of cells, which will develop into the placenta and amniotic membranes. blastocyst An embryo in its very early stage, usually 5 to 6 days old, that has not implanted or attached to a uterus. It is made up of a small group of inner cells, which will develop into the embryo, and an outer layer of cells, which will develop into the placenta and amniotic membranes., a stage in early human embryonic development that occurs within the first four to six days after fertilization. Once hESCs are isolated, the cells may be kept alive and multiplied under specific laboratory conditions. Visit the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine's page on stem cell research to learn more about this process.
The human tissue — typically skin or blood — used to create induced pluripotent stem cell lines is donated by consenting individuals under specific research protocols.
For information about stem cell therapies and the availability of stem cell clinical trials at and beyond UCLA, visit our For Patients and Families page.